Working with GPS Air’s smartIAQ® technology and ASHRAE’s Indoor Air Quality Procedure (IAQP), the school tested whether advanced air cleaning could maintain or improve classroom air while reducing reliance on a dedicated outdoor air system. Lab results confirmed improved air quality and system efficiency, proving that smartIAQ delivers better classrooms with lower equipment and energy demands.

A South Carolina elementary school was considering upgrades to an aging HVAC system; replacing the dedicated outdoor air system (D.O.A.S.) was a primary concern. The school and the consulting engineer considered several approaches, including more ventilation efficiency through ASHRAE 62.1 IAQP.
The original ventilation rate procedure (VRP) design: 160 CFM from the DOAS and 200 CFM from an inroom heat pump. The parties considered eliminating the DOAS wing of the school if smartIAQ was proven able to maintaining or improving classroom air quality.
Prior to decommissioning the DOAS, air quality testing on the VRP design was conducted. smartIAQ, configured as a distributed unit, was installed and DOAS supply to the room turned off. One-week later testing was repeated on the IAQP design. The results indicate air quality improved on critical 62.1 design compounds and many other compounds.
| HVAC Coil on Unit 3 | HVAC Coil on Unit 8 | |||
| Bacteria CFU/in2 | Mold-Fungi CFU/in2 | Bacteria CFU/in2 | Mold-Fungi CFU/in2 | |
| Swab 1 | 30,000,000 | 650,000 | 900,000 | 3,400,000 |
| Swab 2 | 20,000,000 | 500,000 | 20,000,000 | 2,800,000 |
| Swab 3 | 3,100,000 | 3,500,000 | 40,000,000 | 30,000,000 |
| Average | 17,700,000 | 1,550,000 | 20,300,000 | 12,066,667 |
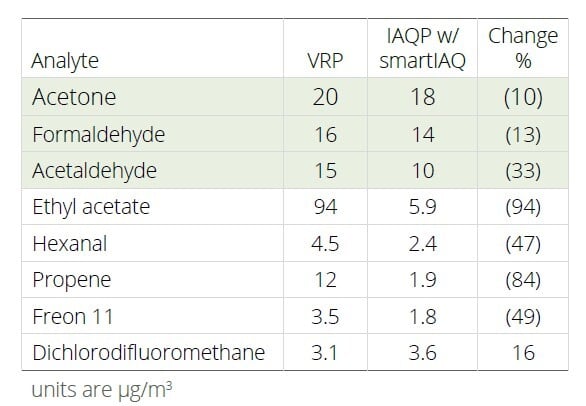
The results align with ASHRAE direction that the IAQP, with effective air cleaning is more efficient and may lead to cleaner indoor air. smartIAQ is proven efficient, effective, and safe for outdoor air reduction, leading to
more cost-effective and simple HVAC systems.
Questions?