Ventilation designs based on the Indoor Air Quality Procedure (IAQP) in ASHRAE Standard 62.1 are lower cost, more efficient, and achieve better indoor air than the Ventilation Rate Procedure (VRP). The IAQP balances outside air with air cleaning to meet air quality needs. Outdoor airflow reductions between 25 and 60% below VRP levels are common with the IAQP. Supported by the International Mechanical Code (IMC) and Uniform Mechanical Code (UMC), the IAQP received increased support from ASHRAE in the 2019, 2022, and 2025 updates to Standard 62.1. The specificity in the Standard overcomes barriers to IAQP adoption, allowing designers to apply the procedure with higher confidence and alignment with ASHRAE.
ASRHAE states:
“The IAQP may allow for a more cost-effective solution to providing good air quality.”
ASHRAE 62.1-2019 User’s Manual
ASHRAE provides the guidance sought by engineers plus updates to Standard 62.1 issues validation requirements for air cleaners. Enter smartIAQ®. - an Intelligent Clean Air System proven by 3rd party testing to the latest standards. smartIAQ uses filtration to extract contaminants and air quality sensing to validate performance and adjust cleaning based on contaminant levels. It responds as needed and reduces speed to extended maintenance intervals when air complies.
Economic benefits of the IAQP begin with downsizing cooling and heating equipment through reducing outside air and continue through lower energy use. When designed in a new building or major renovation, IAQP systems cost less than Ventilation Rate Procedure (VRP) based designs.
HVAC conditioning capacities shrink and equipment is simplified. Since HVAC consumes 40% of a building’s energy and conditioning outdoor air is about 40% of that load, a 50% reduction in outdoor air can save 8% of a building’s energy.
The IAQP is an engineered approach to acceptable building ventilation. It balances contaminant source control, air cleaning, and outdoor air. ASHRAE Standard 62.1 provides a prescriptive approach to reduce design variation and professional risk. The IAQP becomes simple with calculators to apply predictable results. The following table illustrates the progression of the IAQP
from loosely defined to prescriptive and lower risk.
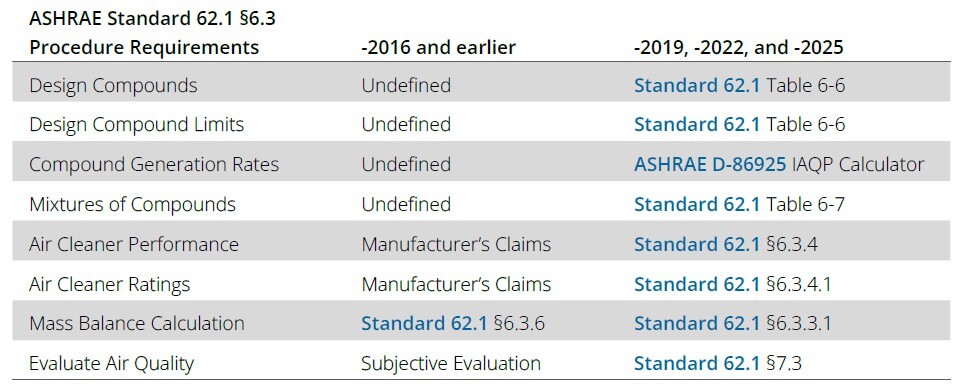
IAQP designs require Mass Balance calculations aligned to the Standard. The smartIAQ Calculator performs the calculations for IAQP ventilation; showing design compound concentrations, outdoor airflow, and air cleaner ratings.
The IAQP applies to most 62.1 spaces. Spaces with higher population densities like classrooms, meeting rooms, houses of worship, auditoriums, and fitness centers have higher potential economic benefit. Designers may selectively apply the IAQP in a VRP design- lowering outdoor airflow selectively in high density spaces within an office or academic space.
smartIAQ complies with the IAQP by removing design compounds from the air when a space is occupied. It modulates cleaning speed from idle to maximum based on contamination in the space. Selecting low speeds when contamination is low leads to extended filter life. Applying high speed with high contamination leads to cleaner indoor air. On demand operation is informed by integrated solid state sensors making smartIAQ is an intelligent clean air system.
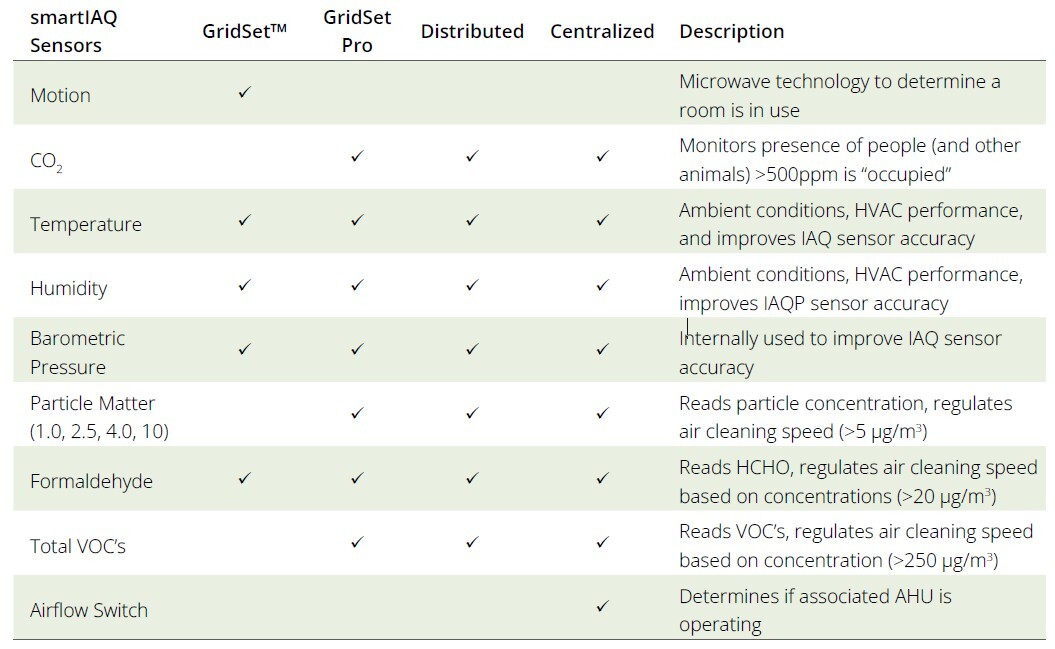
smartIAQ has various operating thresholds, sensor options, and speeds to support a range of applications and budgets. The smartIAQ Calculator (link to request the calculator) demonstrates a specific configurations compliance to the IAQP. Available products and operating modes follow the smartIAQ sensor and product configuration summary table below:
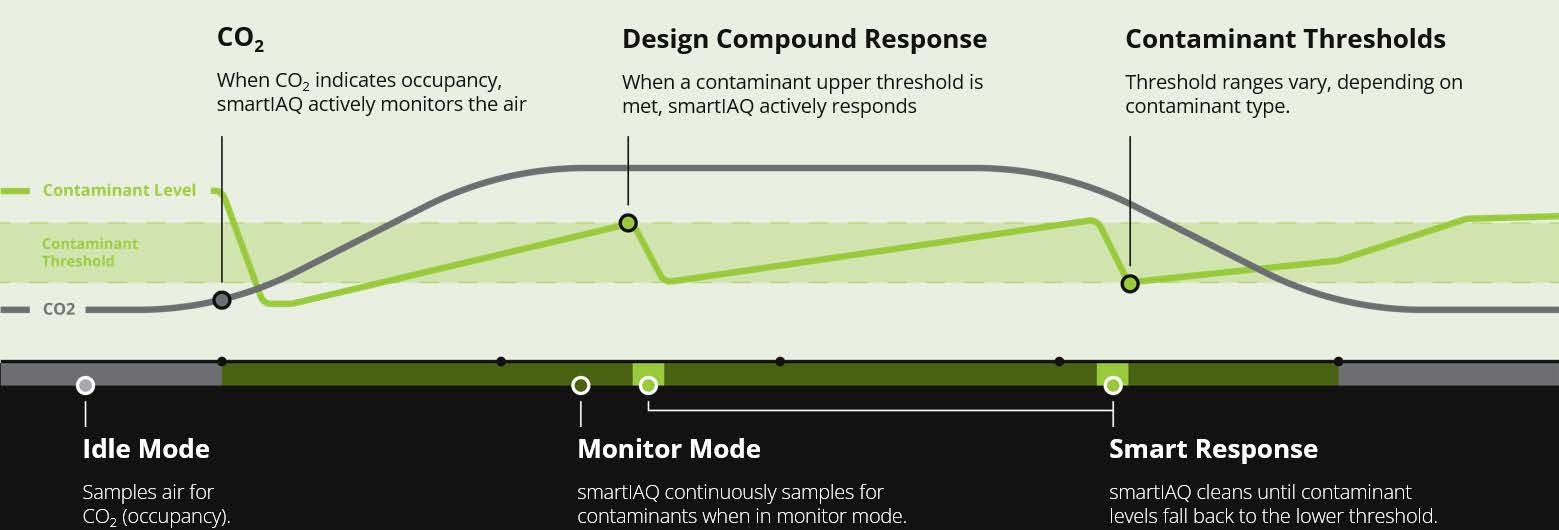
smartIAQ GridSet operates autonomously. Integrated motion detection activates cleaning at 50 CFM. It maintains 50 CFM and modulates speed up to 150 CFM proportional to formaldehyde concentrations over 20 μg/m3 (design limit is 33 μg/m3). In spaces less than 1,500 ft.2 with 10 ft. or lower ceilings, 50 CFM meets the requirements of the IAQP - maintaining all design compounds below design limits. Aligned with Standard 62.1’s formaldehyde focus, smartIAQ GridSet reads formaldehyde for an additional layer of protection. The behavior is mapped below:

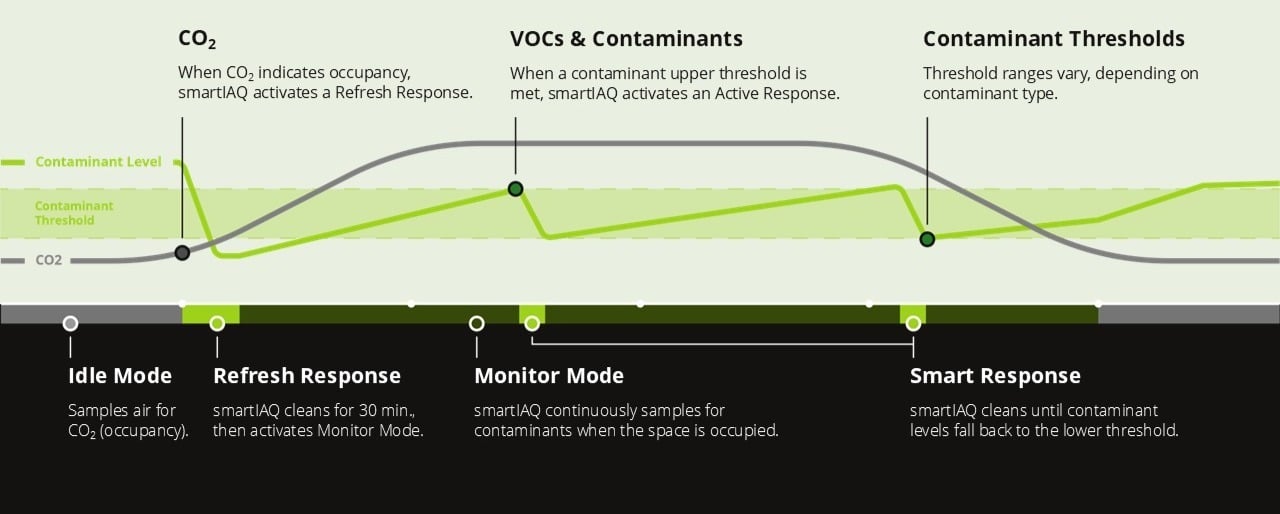
smartIAQ Distributed operates autonomously or responds to a BMS. In standalone operation, it activate cleaning at 150 CFM when CO2 is over 500 ppm. It maintains 150 CFM while a space is occupied and modulates up to 250 CFM (or 500 with-L model) proportional to formaldehyde, PM, and/or TVOC concentrations. smartIAQ Distributed sensing ensures design compounds are extracted when any one compound exceeds thresholds.
smartIAQ Centralized operates when it senses return airflow in the Air Handling Unit (AHU) to which it is coupled. An airflow
switch (provided) activates cleaning at 250 CFM. It may also respond to a BMS. Centralized units clean return air at 250 CFM
and maintain 250 CFM while air is flowing. It modulates up to 700 CFM in response to formaldehyde, PM, and/or TVOC concentrations over thresholds. smartIAQ Centralized reports all sensor readings via BMS (if connected).
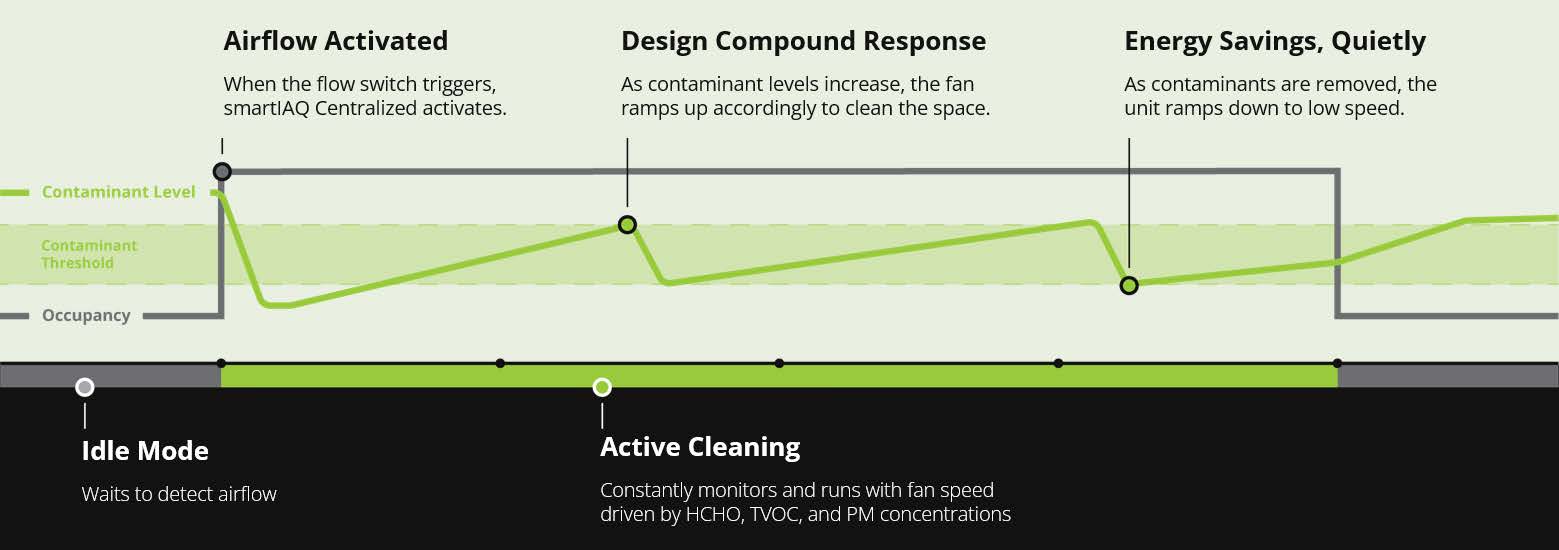
smartIAQ monitors design compound concentration changes in response to its operation. The primary benefit of this closed loop control is confident, traceable IAQP compliance. Additionally, smartIAQ reports when it is unable to lower design compounds despite maximum cleaning speed. In those sustained conditions, smartIAQ provides an air quality alert. Either filters are at end of life or an air quality contaminant has spiked.
If filters are exhausted, filter replacement is the likely resolution to the alert. Expected filter life is 6 and 12 months for Centralized, 1+ year for Distributed, and 2+ years for GridSet. For clients seeking to minimize filter costs and labor, following smartIAQ alerts will extend filters beyond the
expected life in most applications.
smartIAQ GridSet and Distributed systems operate independently of HVAC systems. They extract ambient air, clean it, and return it to the space. A schematic and the appropriate mass balance equation follow:

smartIAQ Centralized systems operate with HVAC systems, cleaning a portion of the returned air. A schematic and the appropriate mass balance equation follow:

The smartIAQ calculator automates the work of iterating through the mass balance calculation. The tool lets operators select one or more smartIAQ units for larger spaces or divide a unit capacity across multiple zones (Distributed and Centralized).
Standard 62.1, Guideline 42, and ASHRAE’s Position Paper on Filtration and Air Cleaners lead to the conclusion that devices used to manage contaminants for the IAQP must be rated for particle and gas phase removal. 62.1 guides manufacturers to rate their products for particle removal under Standard 52.2 - which results in a MERV rating. All other design compound removal (gasses) must be rated under Standard 145.2 - which is a removal efficiency for an individual gas. Standard 62.1 goes further and directs manufacturers to lower the 145.2 determined removal efficiencies for formaldehyde and one non-polar gas to match filter end of life performance. This conservative approach supports IAQP designs for the life of the filter (versus good performance to start and out of spec performance at the end).
smartIAQ has Standard 145.2 ratings for all gaseous design compounds tested at operating airflows, and Standard 52.2 ratings for particles at operating airflows. The smartIAQ Calculator has the end-of-life rated values ensuring compliance with 62.1. All of these tests and results are performed by a 3rd party, and reports are publicly available.
smartIAQ uses standard size filters and may be used with 3rd party filters. Filtration removal efficiency is the rating mechanism for smartIAQ. Therefore, filter selection and IAQP compliance are linked. The values loaded in the smartIAQ calculator are smartIAQ CompleteAQ filter ratings with the end of life rating required by Standard 62.1 for formaldehyde. If other filters meet or exceed the ratings, users may select and use them in smartIAQ. Otherwise it is recommended to run an IAQP calculation with ratings that match the intended filters.
.
If lower rated filters are used in the field, smartIAQ will operate based on sensor input or BMS command and may operate longer and at higher speeds to satisfy contaminants. If filters exhaust quickly or if the sensors detect inadequate air quality it will alert via indicators and/or equipped BMS connection.

smartIAQ CompleteAQ Filters
smartIAQ systems and the smartIAQ Calculator simplify IAQP implementations. smartIAQ is built and validated to the Standard’s requirements and closed loop control provide efficient, long-life operation. With initially lower equipment investment and long maintenance intervals, smartIAQ delivers real return on investment and ongoing energy savings. Operating on the principle of contaminant extraction, smartIAQ’s filters deliver cleaner indoor air while sensors validate performance and compliance.